流程图
请求流程
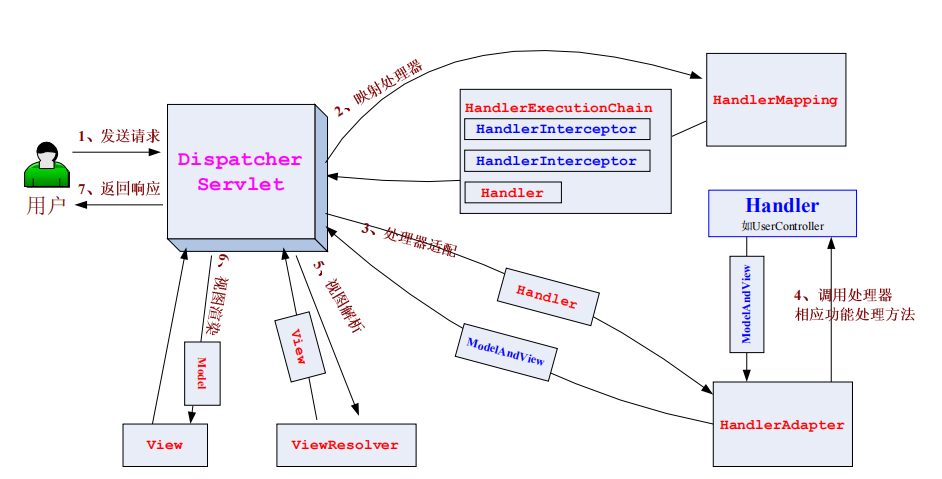
- 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet收到请求调用处理器映射器HandlerMapping。处理器映射器根据请求url找到具体的处理器,生成处理器执行链HandlerExecutionChain(包括处理器对象和处理器拦截器)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet根据处理器Handler获取处理器适配器HandlerAdapter(适配器模式),执行HandlerAdapter处理一系列的操作,如:参数封装,数据格式转换,数据验证等操作
- 处理器Handler(Controller页面控制器)执行完成返回ModelAndView、HandlerAdapter将执行结果ModelAndView返回到DispatcherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器。ViewReslover解析后返回具体View
- DispatcherServlet对View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据model填充至视图中)。
- DispatcherServlet响应用户。
源码
- DispatcherServlet初始化
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
//初始化handlerMappings
initHandlerMappings(context);
//初始化handler适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
RequestMappingHandlerMapping继承自AbstractHandlerMethodMapping(实现了InitializingBean接口)会从applicationContext中扫描bean,并检测注册handler methods.
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java:
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
/**
* Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods.从applicationContext中扫描bean,并检测注册handler methods
* @see #getCandidateBeanNames()
* @see #processCandidateBean
* @see #handlerMethodsInitialized
*/
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
//遍历所有bean
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
//扫描注解
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
//打印扫描到多少mappings的日志
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
//根据bean名获取bean的class
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
...
}
//如果是handler则检测handler methods
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
/**
* Look for handler methods in the specified handler bean.
* @param handler either a bean name or an actual handler instance
* @see #getMappingForMethod
*/
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
//获取handler class
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
//可用的handler class
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
//遍历handler的method,获取method的映射([ControllerName]#[MethodName])
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
//获取method的映射
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
...
//遍历handler methods映射
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
//获取可执行的方法,类本身方法还是接口方法(spring代理)
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
//注册mapping到mappingRegistry
//方法存储url->mapping,maping->HandlerMethod的映射
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
RequestMappingHandlerMapping.java:
@Override
@Nullable
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
//方法上的
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
//类上的
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
//合并requestMappingInfo,它的name就是[ControllerName]#[MethodName]
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
//增加路径前缀,如context-path这些吧
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
//requestMappingInfo的paths就是url的请求路径
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
@Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
//扫描RequestMapping及包含它的注解的类或方法,并构造RequestMappingInfo
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
- DispatcherServlet的doDispatch方法如下
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
//处理器执行链
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//如果是上传请求,转化为MultipartHttpServletRequest
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
//查找handler执行链
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
//查找handler适配器
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//前置拦截器
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
//通过handler适配器,执行handler方法,获取模型视图
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//如果没有view视图,设置默认视图
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//后置拦截器
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//渲染视图
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
2.DispatcherServlet获取handler执行链
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
3.DispatcherServlet获取handler适配器
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
4.执行方法源码分析
/**
* 获取参数,执行方法最外层的调用
* 源码位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.handle(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, Object)
*/
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
// 直接调用这个方法
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
/**
* 获取参数,执行方法内部的调用逻辑
* 源码位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.handleInternal(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, HandlerMethod)
*/
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
// 检查当前请求的method是否为支持的method(默认Null,可通过继承AbstractController设置supportedMethods)
// 检查当前请求是否必须session (默认false,可通过继承AbstractController设置requireSession)
checkRequest(request);
/**
* 判断当前是否需要支持在同一个session中只能线性地处理请求:一个session同时只能处理一个线程
* 因为锁是通过 synchronized 是 JVM 进程级,所以在分布式环境下,
* 无法达到同步相同 Session 的功能。默认情况下,synchronizeOnSession 为 false
*/
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
// 获取当前请求的session对象
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
// 为当前session生成一个唯一的可以用于锁定的key
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
// 对HandlerMethod进行参数等的适配处理,并调用目标handler
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// 如果当前不存在session,则直接对HandlerMethod进行适配
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// *如果当前不需要对session进行同步处理,则直接对HandlerMethod进行适配
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
//判断当前请求头中是否包含Cache-Control请求头,如果不包含,则对当前response进行处理
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
// 如果当前SessionAttribute中存在配置的attributes,则为其设置过期时间。
// 这里SessionAttribute主要是通过@SessionAttribute注解生成的
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
// 如果当前不存在SessionAttributes,则判断当前是否存在Cache-Control设置,
// 如果存在,则按照该设置进行response处理,如果不存在,则设置response中的
// Cache的过期时间为-1,即立即失效
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
/**
* 获取参数,执行方法前的准备逻辑
* 源码位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, HandlerMethod)
*/
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
// 把我们的请求req resp包装成 ServletWebRequest
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
// 获取容器中全局配置的InitBinder和当前HandlerMethod所对应的Controller中
// 配置的InitBinder,用于进行参数的绑定
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
// 获取容器中全局配置的ModelAttribute和当前HandlerMethod所对应的Controller 中配置的ModelAttribute,
// 这些配置的方法将会在目标方法调用之前进行调用
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
// 封装handlerMethod,会在调用前解析参数、调用后对返回值进行处理
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
// 让invocableMethod拥有参数解析能力
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
// 让invocableMethod拥有返回值处理能力
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
// 让invocableMethod拥有InitBinder解析能力
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
// 设置ParameterNameDiscoverer,该对象将按照一定的规则获取当前参数的名称
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
// ModelAndView处理容器
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
// 将request的Attribute复制一份到ModelMap
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
// *调用我们标注了@ModelAttribute的方法,主要是为我们的目标方法预加载
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
// 重定向的时候,忽略model中的数据 默认false
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
// 获取当前的AsyncWebRequest,这里AsyncWebRequest的主要作用是用于判断目标
// handler的返回值是否为WebAsyncTask或DeferredResult,如果是这两种中的一种,
// 则说明当前请求的处理应该是异步的。所谓的异步,指的是当前请求会将Controller中
// 封装的业务逻辑放到一个线程池中进行调用,待该调用有返回结果之后再返回到response中。
// 这种处理的优点在于用于请求分发的线程能够解放出来,从而处理更多的请求,提高吞吐。
// 只有待目标任务完成之后才会回来将该异步任务的结果返回。
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
// 封装异步任务的线程池、request、interceptors到WebAsyncManager中
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
// 这里就是用于判断当前请求是否有异步任务结果的,如果存在,则对异步任务结果进行封装
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
// *对请求参数进行处理,调用目标HandlerMethod,并且将返回值封装为一个ModelAndView对象
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
// 对封装的ModelAndView进行处理,主要是判断当前请求是否进行了重定向,如果进行了重定向,
// 还会判断是否需要将FlashAttributes封装到新的请求中
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
/**
* 获取参数,执行方法
* 源码位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest, ModelAndViewContainer, Object...)
*/
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
/*真正的调用我们的目标对象 很重要 很重要*/
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
// 设置相关的返回状态
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
// 如果请求处理完成,则设置requestHandled属性
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
// 如果请求失败,但是有错误原因,那么也会设置requestHandled属性
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
// 遍历当前容器中所有ReturnValueHandler,判断哪种handler支持当前返回值的处理,
// 如果支持,则使用该handler处理该返回值
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
5.渲染视图源码
/**
* 渲染视图逻辑
* 源码位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, HandlerExecutionChain, ModelAndView, Exception)
*/
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
// 异常视图
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
// 解析、渲染视图:解析视图名,拼接前后缀
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled.. 拦截器:AfterCompletion
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}